Key Takeaways
- Excessive use of chemical fertilizers in China has led to environmental issues, prompting the promotion of organomineral fertilizers (OMF).
- Digital Agricultural Technology Extension Services (DATES) have shown potential in increasing OMF adoption rates among farmers.
- The effectiveness of DATES varies by farming household characteristics, indicating a need for targeted policy strategies.
Mineral fertilizers are essential for food security, but their overuse has resulted in various environmental challenges in China, including soil nutrient imbalance, reduced fertility, and water pollution. In response, organomineral fertilizers (OMF) have been introduced as a greener alternative, combining organic materials with a small proportion of mineral fertilizers to enhance crop yield and quality while mitigating environmental damage. Despite their benefits, the adoption of OMF has been low, particularly among smallholder farmers who often lack awareness and understanding of the fertilizer.
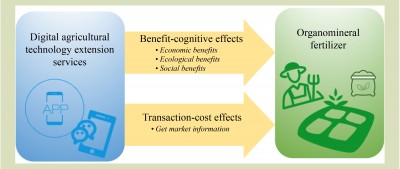
Recent research by Professor Minjuan Zhao and her team from Northwest A&F University aims to address this issue. They examined the impact of Digital Agricultural Technology Extension Services (DATES) on the adoption of OMF among apple farmers in Shaanxi and Gansu provinces. Utilizing Internet platforms like WeChat and mobile applications, DATES facilitates access to agricultural knowledge, overcoming limitations associated with traditional extension methods.
The survey covered 1,167 apple-growing households, revealing that many farmers still believe “the more fertilizer applied, the higher the yield,” leading to excessive use of mineral fertilizers. This practice not only threatens food safety but also poses risks to public health and the environment. Findings indicated that farmers utilizing DATES are between 7.2% and 10.2% more likely to adopt OMF than those who do not, with the adoption intensity of OMF rising from 7.0% to 9.9% among DATES users.
This study highlights that DATES plays a critical role in enhancing farmers’ understanding of OMF’s value. Users of DATES gained better insights into the economic, ecological, and social benefits of OMF. Additionally, DATES lowers the cost of accessing agricultural information, thus reducing the risks associated with trying new technologies and motivating farmers to adopt OMF.
Moreover, the effectiveness of DATES varies based on the farmers’ social and economic characteristics. Farmers with enhanced social capital experience quicker information dissemination and lower learning costs, leading to a higher adoption of OMF. Conversely, those in better economic conditions are more equipped to bear risks and invest in new technologies. This suggests that policies need to account for the diversity among farming households and include targeted strategies.
The research advocates for strengthening digital agricultural infrastructure in rural areas to improve DATES accessibility. It promotes a mixed approach combining online and offline channels to disseminate knowledge on green production techniques. Differentiated strategies should be developed to assist farmers at various levels of social capital and economic status, focusing on empowering responsive farmers as role models while supporting less responsive farmers in overcoming financial and informational barriers.
The content above is a summary. For more details, see the source article.