Key Takeaways
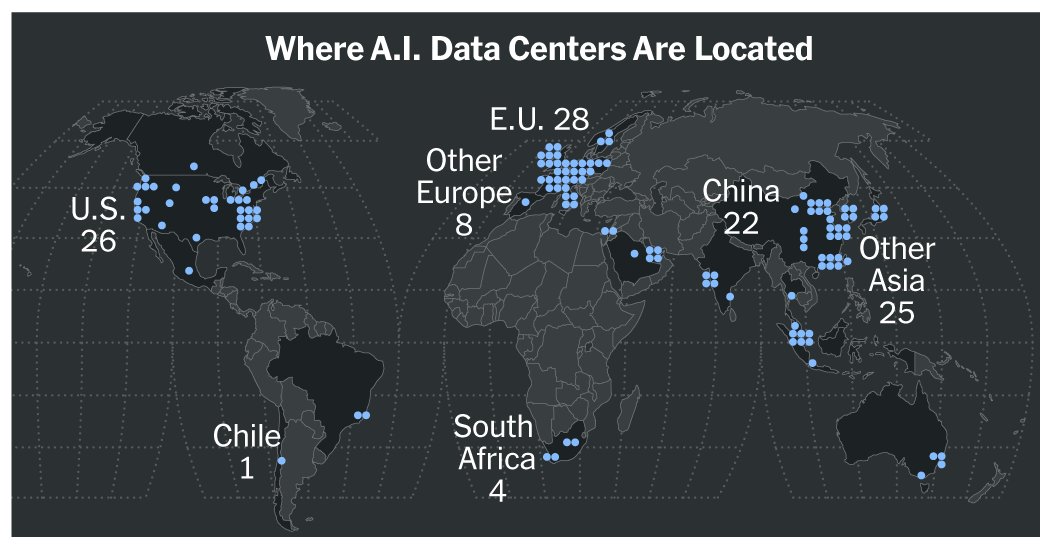
- Only 32 nations, mainly in the Northern Hemisphere, have A.I.-specialized data centers, creating a significant global digital divide.
- The U.S. and China dominate A.I. infrastructure, with over 90% of global data centers located in these countries.
- Countries with limited A.I. resources face challenges in scientific research and economic growth, prompting efforts to build local infrastructure for A.I.
A.I. Data Center Divide
A recent analysis highlights a growing digital divide in artificial intelligence (A.I.) technology, with only 32 countries possessing specialized data centers. This has resulted in significant disparities in computing power between nations, predominantly benefiting the United States, China, and the European Union, which host over half of the world’s most advanced A.I. computing hubs.
The project, spearheaded by Sam Altman of OpenAI, encompasses a $60 billion A.I. data center in Texas, set to become a leading computing hub. In stark contrast, countries like Argentina struggle with outdated facilities. Nicolás Wolovick, a computer science professor there, indicates a sentiment of loss due to the disparity in technological resources.
This divide influences geopolitics and economic climates, leading to dependencies on A.I. tech from the U.S. and China. Approximately 90% of significant data centers are owned by American and Chinese firms, with Africa and South America significantly lagging; many countries lack any A.I. hubs altogether.
The scale of modern A.I. data centers far exceeds earlier computing facilities, requiring considerable financial investment and infrastructure that many developing nations cannot sustain. Access to data centers is critical for advancements in various sectors, including healthcare and defense. Meanwhile, nations with limited A.I. capabilities face significant challenges, compromising their scientific progress and economic development. Officials express concerns over the growing reliance on international corporations for vital computing resources.
As the race for A.I. capabilities intensifies, several regions are striving to secure local A.I. projects. For instance, India supports the development of A.I. models in local languages, while Brazil is investing $4 billion in A.I. initiatives. The European Union has launched a €200 billion plan for new A.I. data centers to combat reliance on American technology.
Efforts to establish “sovereign A.I.” are underway globally, with notable projects like Cassava, a tech firm in Africa poised to build advanced data centers to address local demand. However, experts warn that without substantial investment and innovation, countries might struggle to keep pace with the ongoing A.I. revolution.
Overall, the widening gap in A.I. capabilities raises urgent questions about future digital sovereignty and equitable access to cutting-edge technology.
The content above is a summary. For more details, see the source article.